Dissolved Oxygen is the amount of oxygen (O2) present in water, and just like humans, plants need oxygen to survive and thrive. It is one of the key factors in the growth and health of plants. Dissolved Oxygen is measured in milligrams per liter (mg/L), parts per million (ppm), or as a saturation percentage. It is affected by various factors, including water temperature, salinity, and the presence of other dissolved gases such as carbon dioxide. In this article, I will discuss the benefits of Dissolved Oxygen for plants and how to optimize its levels.
Coming soon!
What is Dissolved Oxygen? |  |
| Dissolved Oxygen and its relationship to plant lifeFirst and foremost, Dissolved Oxygen is essential for the respiration process of plants. The roots of plants require oxygen for aerobic respiration, which is the process of releasing energy from glucose molecules. This energy is then used by the plant to carry out essential biological functions, including the growth and development of roots, stems, and leaves. When there is not enough oxygen in the water, the plant roots may not be able to access enough oxygen to carry out aerobic respiration. This can lead to root damage, slower growth, and smaller yields, which can have a negative impact on the overall health of the plant. In addition, low oxygen levels can also promote the growth of harmful microorganisms in the water or soil, which can further damage the roots and can lead to disease or the plant's death. Conversely, if the level of Dissolved Oxygen is too high, it can also be detrimental to plant growth. High levels of Dissolved Oxygen can lead to the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can cause damage to plant cells and tissues. |
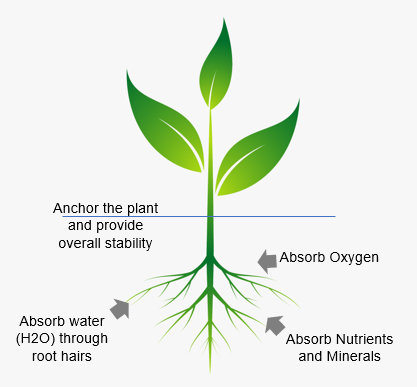
Reduce fertilizers and pesticidesIn addition to promoting healthy plant growth, optimizing the levels of Dissolved Oxygen can also reduce the need for fertilizers and pesticides. When plants have access to sufficient oxygen, they are better able to absorb and utilize the nutrients present in the soil or water. This means that less fertilizer is needed to achieve the same level of growth and yield. Similarly, plants that are healthy and strong due to optimal Dissolved Oxygen levels are more resistant to pests and diseases, reducing the need for pesticides and fungicides. The roots of plants absorb water and nutrients from the soil, and this process requires energy. When the levels of Dissolved Oxygen are low, the energy required for nutrient uptake is not available, leading to poor absorption of essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. This can result in nutrient deficiencies, poor growth, and low yields. In contrast, correctly optimized levels of Dissolved Oxygen can promote healthy root growth and increase the plant's ability to better absorb nutrients. | 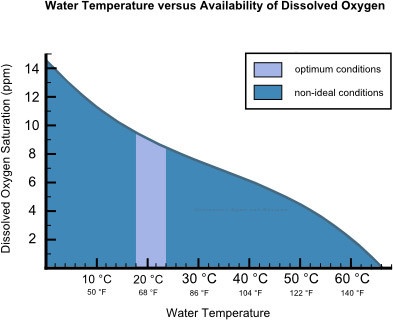 |
 | How can Dissolved Oxygen levels be optimized and controlled?There are several ways to optimize and control the levels of Dissolved Oxygen in water used for plants. The first step is to measure the levels of Dissolved Oxygen using a DO meter. This will help you determine if the levels are too low and need to be increased. The second step is to improve the level of Dissolved Oxygen. An easy way to increase Dissolved Oxygen is through aeration or agitation. This involves introducing air into the water, which increases oxygen levels. This method can generally be considered to be the easiest and safest way. Another method is using oxygen injection, where pure oxygen is added to the water to increase oxygen levels. However, this method can be expensive and needs to be fully controlled, therefore it's usually only reserved for large commercial growers. |
Proper Irrigation PracticesWhen using living soil or mediums like coco, overwatering can easily lead to waterlogging, which can quickly reduce the amount of oxygen available to plant roots and kill the plant. Good irrigation practices, including watering plants when the soil is dry and ensuring good drainage, can help to maintain adequate oxygen levels in the soil. Aerating the soil or coco substrates can also prevent waterlogging. Aeration is the process of introducing air into the soil to increase Dissolved Oxygen levels. This can be achieved through various methods, including adding amendments to the soil, the use of oxygenating agents, or mechanical aeration, which involves using machines to create Aeration channels in the soil. Soil compaction can also reduce the amount of air space in the soil, which can also limit the amount of oxygen available to plant roots. Avoiding soil compaction through practices such as reducing foot traffic and minimizing the use of heavy equipment can also help to maintain adequate oxygen levels in the soil. |  |
ConclusionDissolved Oxygen is a critical component of plant growth and survival. Maintaining appropriate levels of Dissolved Oxygen is essential to ensure healthy root growth and overall plant health. By understanding the importance of Dissolved Oxygen and implementing proper management practices, cultivators and farmers can optimize their plant growth and productivity. |